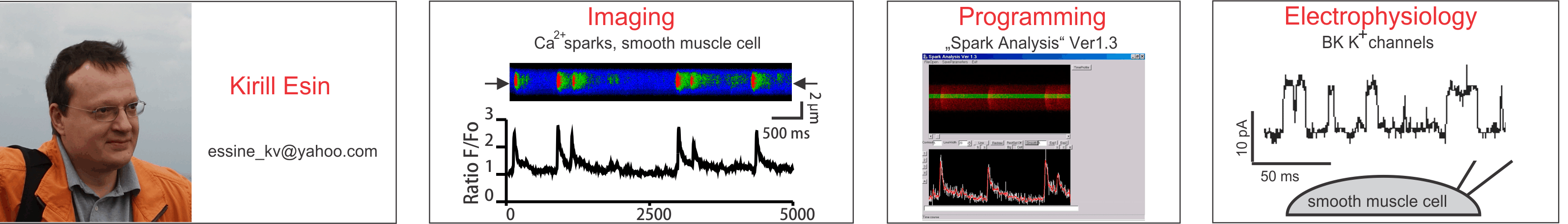
| Imaging | ||||
| Programming | ||||
| Electrophysiology | ||||
| Teaching | ||||
| Microscopy & image processing | ||||
| Programming | ||||
Live cell imaging by conventional and spinning disk confocal microscopy
Mouse Cardiomyocyte
|
|||
Mouse Oocytes
|
|||
C.elegans Pharynx
|
|||
Rat Arterial Smooth Muscle Cell
|
|||
Human Blood Neutrophil fMLP, a proinflammatory N-formylated peptide released by bacteria, induces intracellular calcium rise in a human blood neutrophil (Perkin Elmer, UltraView LCI laser spinning disk confocal microscope; calcium sensitive fluorescent dye Fluo-4 AM; Essin_K_AJP_2007.pdf, Fig 3.). |
|||
Mouse Rod Bipolar Cell Depolorization-induced increase in intra-bouton calcium concentration in a mouse rod bipolar cell. Cell soma and synaptic boutons are seen at the left and right sides of the up video, respectively (Andor iXON camera attached to a light microscpe; calcium sensitive fluorescent dye Fluo-8 loaded via a somatic patch pipette). The time course of intra-bouton calcium changes is present in the bottom video Mouse_Retinal_Slices_Method.zip |
|||
| Kirill Esin, essine_kv@yahoo.com |